- Home
-
Main Instruments
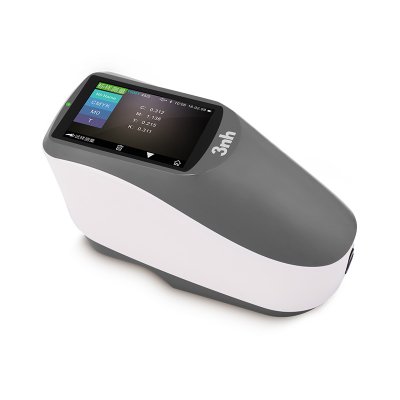
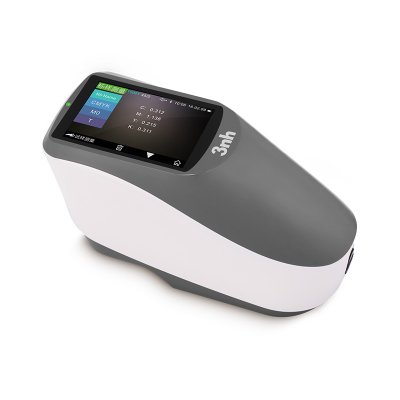
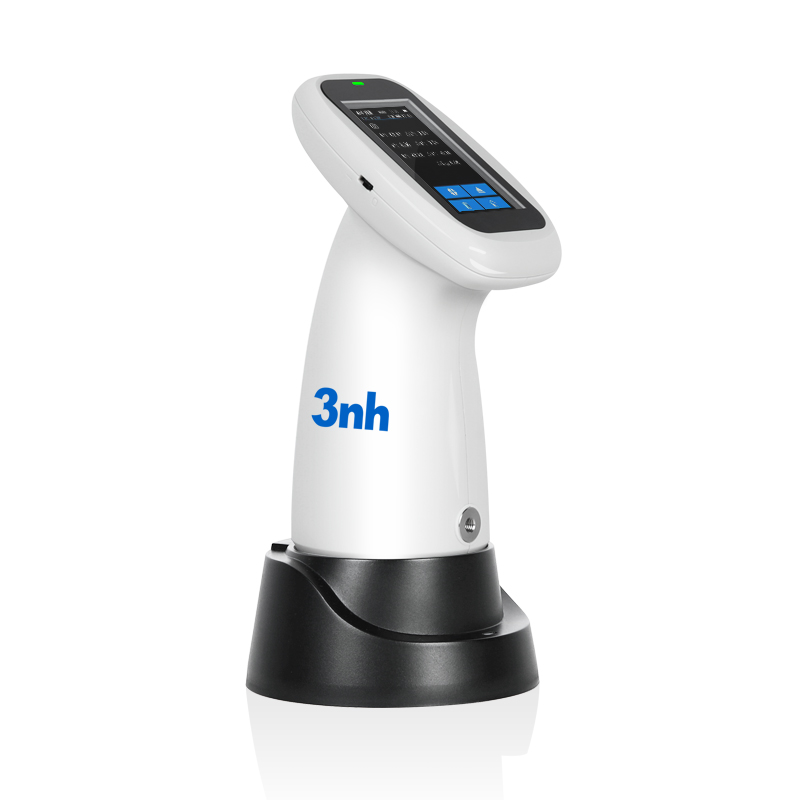
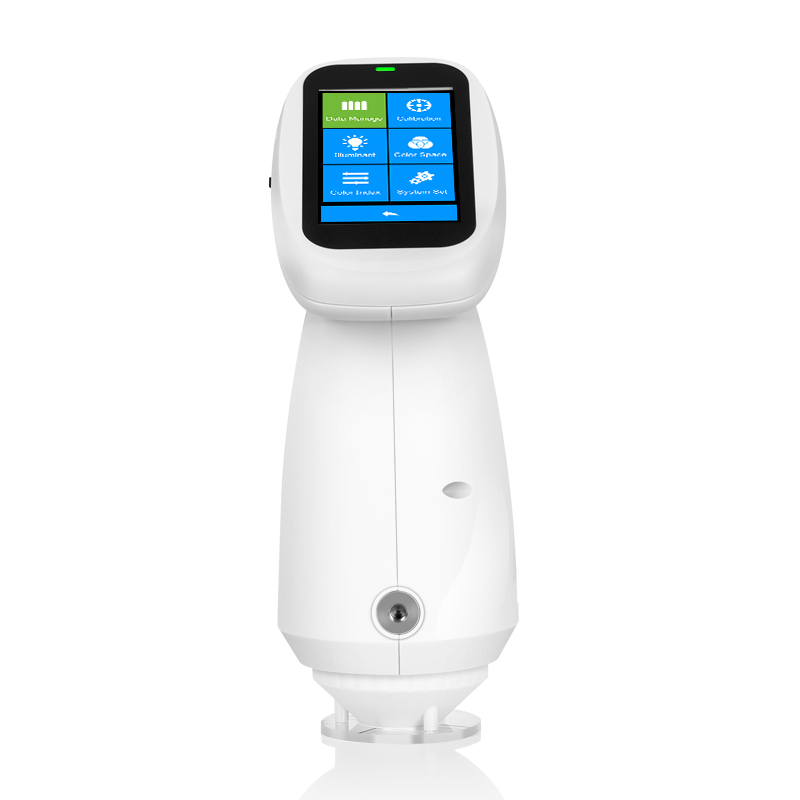
TS8450 Portable Desktop Spectrophotometer
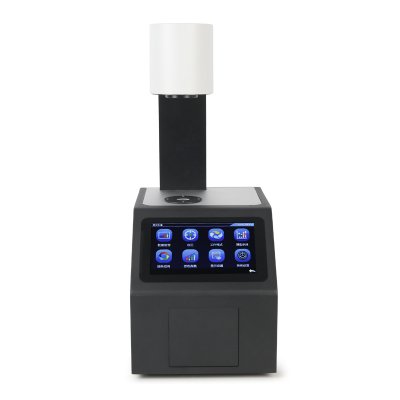
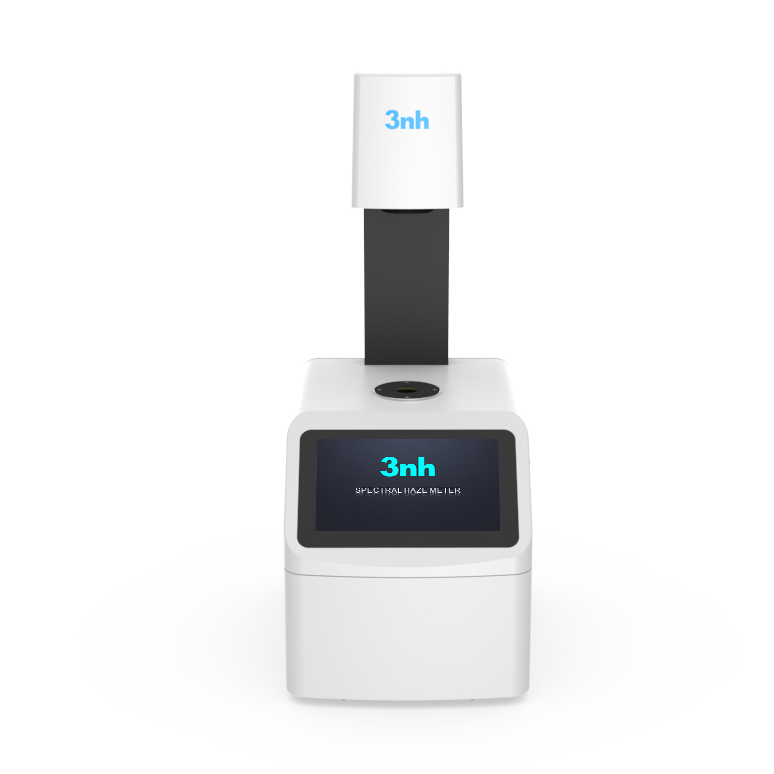
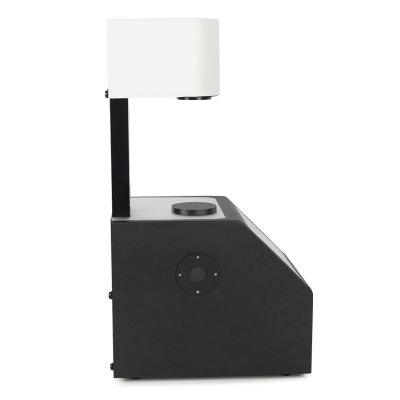
Benchtop Spectrophotometer YS6060
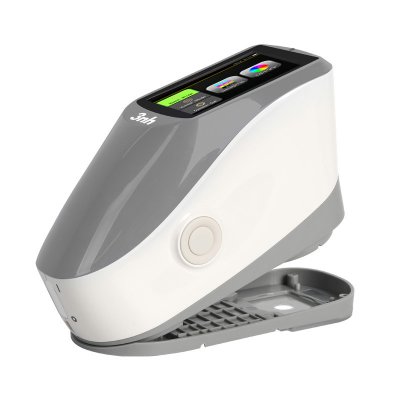
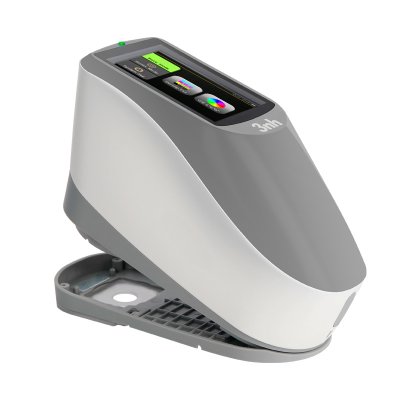
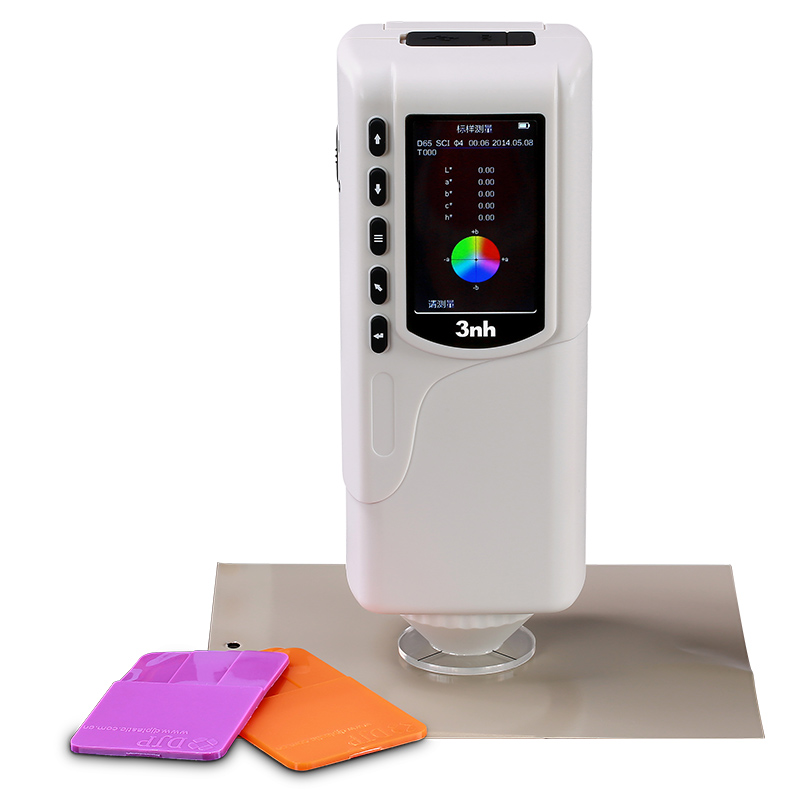
TS8280 Portable Desktop Spectrophotometer
TS8260 Portable Desktop Spectrophotometer
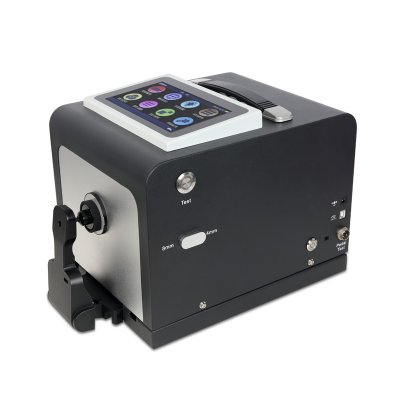
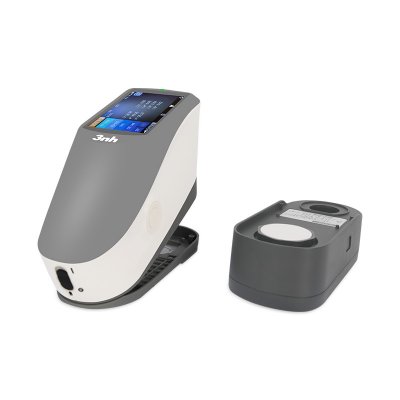








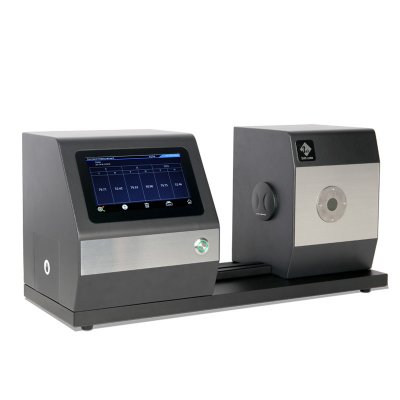
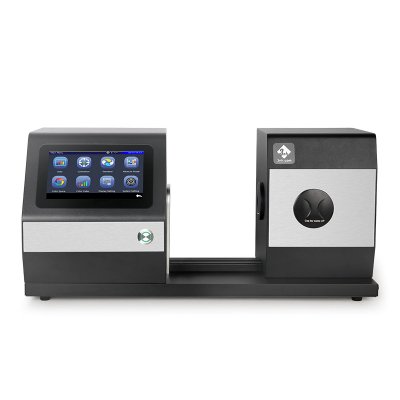
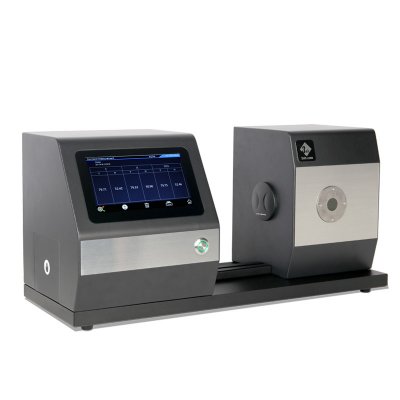
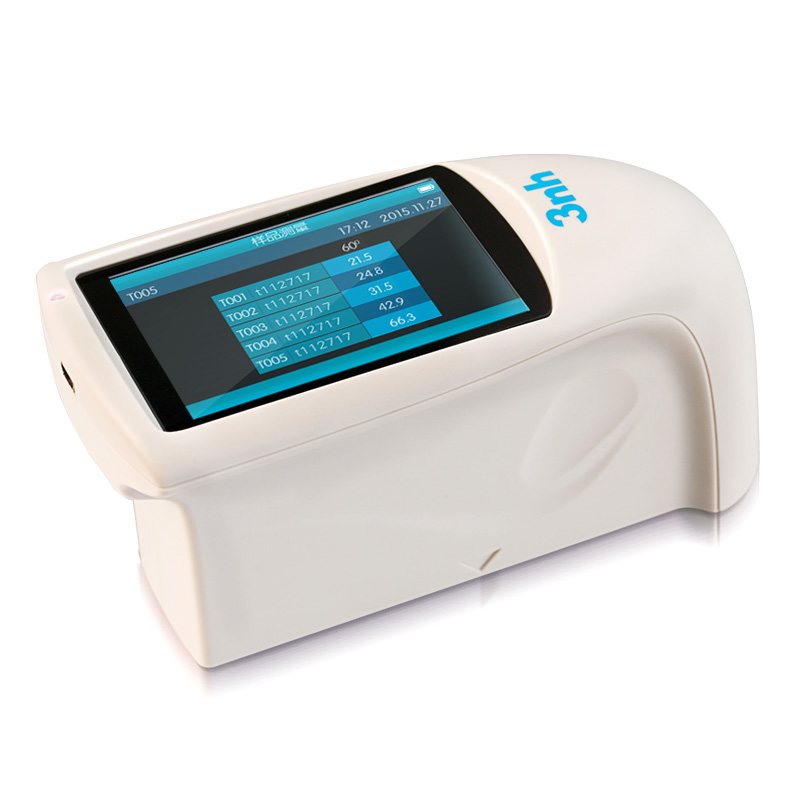
MS3012 Multi-angle spectrophotometer
MS3008 Multi-angle spectrophotometer
MS3006 Multi-angle spectrophotometer










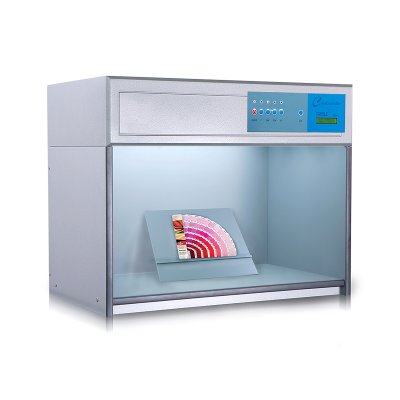
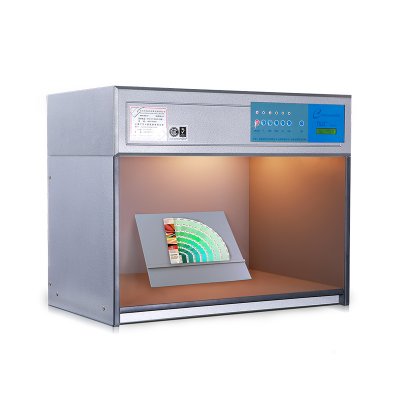
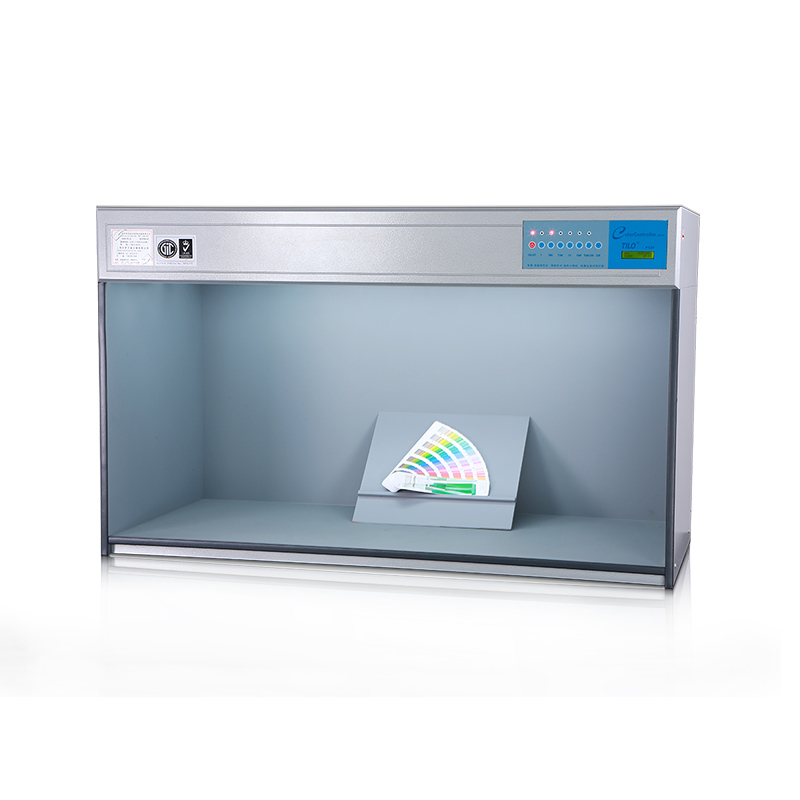
M60 American color light booth
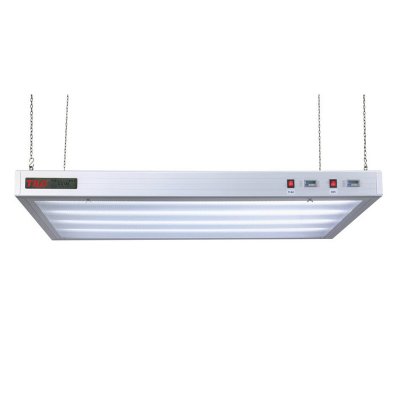
CC120-W Hanging Light Booth Viewer
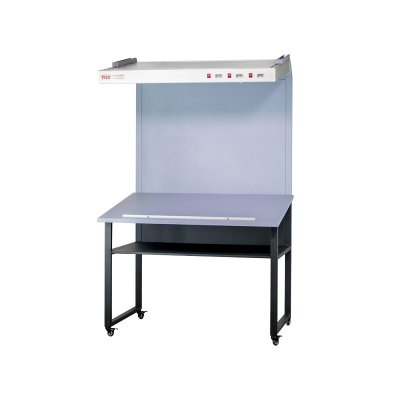
CC120 Color Viewer Light Table








Sector Star Test Chart (36 cycles)
Sector Star Test Chart (72 cycles)
Streaking Measurement Test Chart











-
Innovative Solution
Building and Decorative Materials
Agricultural Products and Food
In the textile production process, color consistency is a complex and easily affected by a variety of factors, and color testing and management is the core to ensure product quality and consistency.

In automotive manufacturing and automotive parts manufacturing, color consistency and accuracy is critical because it directly affects the appearance of the vehicle, brand image and customer satisfaction.

In the plastics industry, color measurement is crucial, mainly in ensuring product consistency, maintaining brand image, strengthening quality control and enhancing customer satisfaction.

Color management in coatings is key to maintaining product quality and competitiveness in the marketplace.

Color management in the building and decorative materials industry is crucial for ensuring the aesthetic appeal, consistency, and market competitiveness of products.

Color management of medical materials is key to ensuring product functionality and safety.

In the cosmetics industry, color testing is key to ensuring product quality and brand image, and is critical to product development and market performance

Color testing plays a key role in the produce and food industry because color not only affects the appearance and attractiveness of a product, but also reflects its quality and freshness.

The importance of management in the packaging, printing and paper products industry is reflected in several key areas.

Imaging Test Laboratory Solutions, Sine Image’s customized imaging test laboratory is equipped with wide-angle test light boxes, 7 sets of fixed color temperature test light boxes, various test charts (such as skin tone test charts, resolution test charts, distortion test charts, real-scene subjective test charts, etc.), chart holders, fill lights, and other equipment. Its testing solutions and products are widely used in industries such as security monitoring, automotive imaging, photography, medical imaging, televisions and computers, mobile phones, and drones for image quality inspection.

-
Service&Support
Frequently Asked Question about Appearance&Color Measuring Instruments,On this page you will find a few frequently asked questions that are relevant for the vast majority of our Measurment Instruments equipment.

Catalogues, Brochures, Flyers, Certificates, Technical information and more; Any document requirement please download here to achieve well understanding for Color Spectrophotometer, Gloss Meter, Color assessment cabinet products, Threenh Technology is a precision instrument company dedicated to research and development, production, sales, and technical services.

Account Name: Guangdong ThreeNH Technology Co., Ltd. Account NO: 6652 7828 9156 Bank Name: BANK OF CHINA LIMITED GUANGZHOU ZENGCHENG SHITAN SUB-BRANCH

IQstest is an image testing software developedby 3nh‘s SINE IMAGE company, Have many yearsof experience in image inspection, supporting Resolution Charts、ComprehensiveCharts、Dynamic Range Charts、Gray Step Charts、Distortion Charts、ColorChecker、White、Balance Charts、Fov Charts、Custom Charts.

color matching software

3NH Warranty Terms; Guangdong Threenh Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “3NH”) provides a limited period of warranty service to clients (hereinafter referred to as “client”) who have purchased products manufactured by 3NH (hereinafter referred to as “Product”) in accordance with the terms of this Warranty Policy (hereinafter referred to as “3NH”).

-
Resources
3NH Company News Center, News and Events, Exciting Developments,our news center serves as a dynamic hub of the latest happenings and developments within the company and the industry we thrive in. Here, you will gain exclusive insights into our continuous pursuit of innovation and excellence. Color Management Leader 3NH The Latest News

The Latest Product News from the Leaders in Color Management

Discover the latest tech news and measurement products from threenh technology. Shop innovative tech solutions or measurement instruments for your business now!

Get essential Basic color Knowledge with threenh Technolgy. Explore smart solutions for your business needs. Contact us today!

3NH Industry News Center, News and Events, Exciting Developments,our News Center serves as a dynamic hub of the latest happenings and developments within the industry we thrive in. Here, you will gain exclusive insights into our continuous pursuit of innovation and excellence.

-
About Threenh
Embark on a virtual journey through our state-of-the-art manufacturing facility. Witness the precision and efficiency of our production lines as they bring to life our high-quality instrumentations and other advanced products.

- Contact